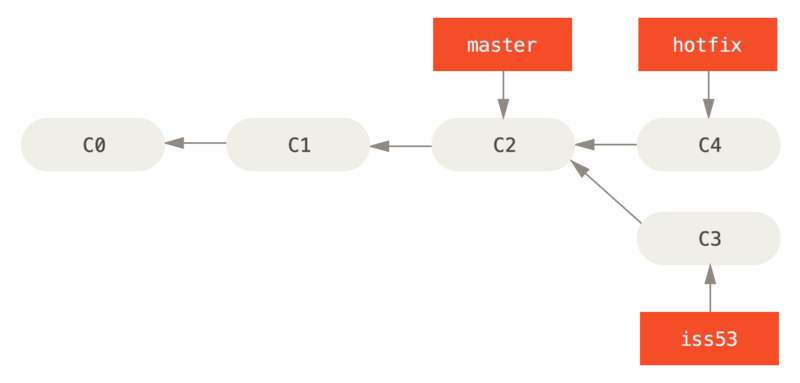
master
You can run your tests, make sure the hotfix is what you want, and merge it back into your
masterbranch to deploy to production. You do this with the git merge command:$git checkout master$git merge hotfixUpdating f42c576..3a0874cFast-forwardindex.html | 2 ++1 file changed, 2 insertions(+)
You’ll notice the phrase “fast-forward” in that merge. Because the commit pointed to by the branch you merged in was directly upstream of the commit you’re on, Git simply moves the pointer forward. To phrase that another way, when you try to merge one commit with a commit that can be reached by following the first commit’s history, Git simplifies things by moving the pointer forward because there is no divergent work to merge together – this is called a “fast-forward.”
Your change is now in the snapshot of the commit pointed to by the
master branch, and you can deploy the fix.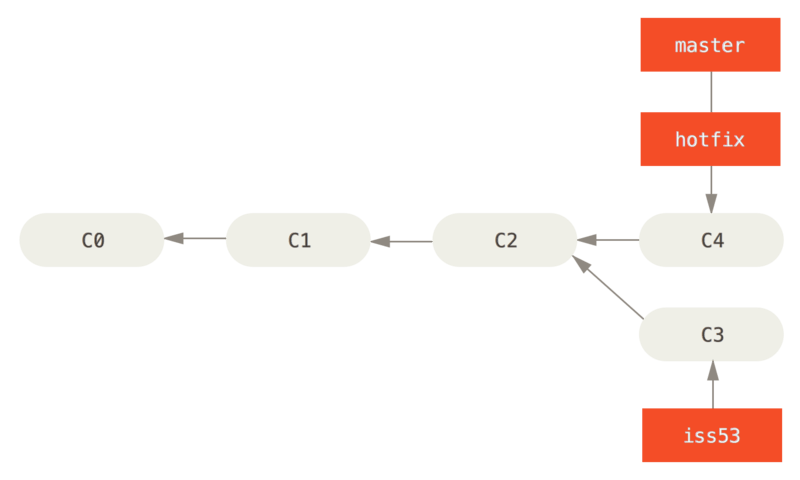
master is fast-forwarded to hotfix
reference: https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Git-Branching-Basic-Branching-and-Merging
No comments:
Post a Comment